Buckeye Institute Analysis Finds Nearly 116,000 Ohioans Would Lose Jobs Under D.C. Imposed $15 Minimum Wage
Mar 04, 2021Columbus, OH – On Thursday, The Buckeye Institute released an analysis using data from the non-partisan Congressional Budget Office (CBO) to estimate the impact of a $15 an hour minimum wage proposal included in the Raise the Wage Act of 2021. The analysis found that nearly 116,000 Ohio workers would lose their jobs if the federal wage hike is imposed (see the chart below or download a PDF).
“While some individuals would benefit from a federally imposed minimum wage hike, it is clear from The Buckeye Institute’s analysis that many others—nearly 116,000 Ohioans—would suffer job loss,” said Logan Kolas, an economic policy analyst with the Economic Research Center at The Buckeye Institute who conducted the analysis. “Thousands of Ohio’s small business owners—many who have been devastated by the pandemic—will be forced to cut jobs or be put out of business by this misguided attempt to forcibly raise wages. The result will be fewer jobs for Ohioans. The better policy is to leave minimum wage decisions to the states to ensure that local economies can grow, create more jobs, and hire more workers.”
The Economic Research Center’s analysis was conducted by applying the CBO findings—which estimated that 5.2 percent of workers earning a little more than $15 an hour or less than $15 an hour would lose their job if the minimum wage increase was imposed—to Ohio Census Bureau regions (the most reliable available data on how much workers make in that region) to estimate the minimum number of jobs lost by 2025, when the proposed wage hike would fully take effect. The Buckeye Institute analysis shows that nearly 116,000 Ohioans would lose their jobs if Congress adopts this $15 an hour minimum wage hike.
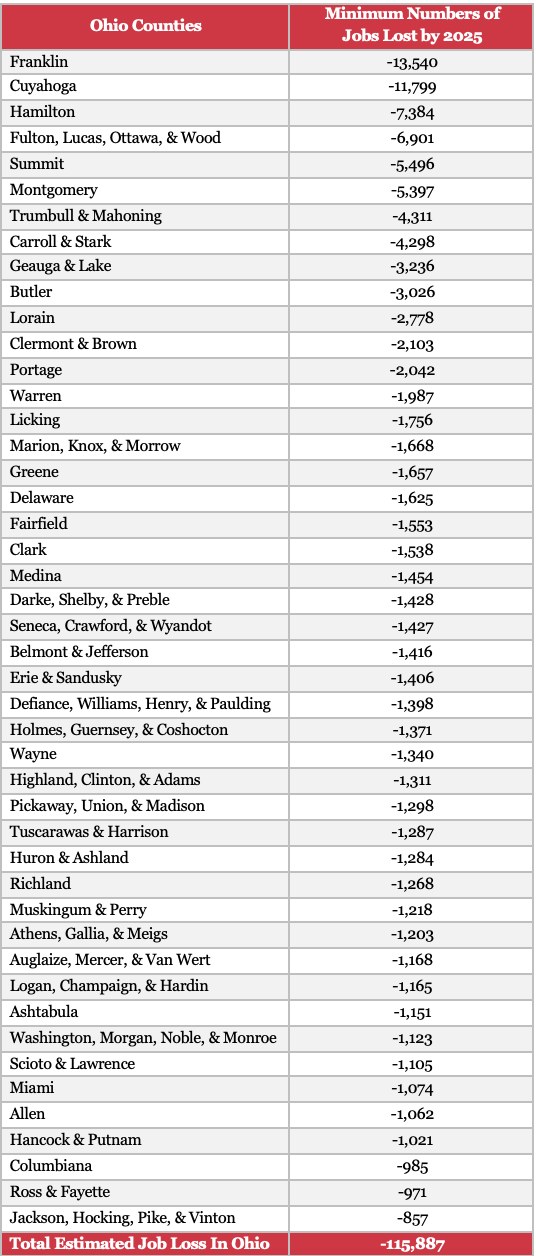
Notes: Due to data limitations, if more than one county is listed, the minimum number of jobs lost is the total amount of jobs lost in all of those counties combined.
Sources: Economic Research Center calculations are from Congressional Budget Office, The Budgetary Effects of the Raise the Wage Act of 2021, February 8, 2021; PUMS USA, University of Minnesota, www.ipums.org.
# # #
